Media
HKU researchers generate tomatoes with enhanced antioxidant properties by genetic engineering
09 Nov 2017

(from left) Dr Wang Mingfu, Professor Chye Mee-len and Dr Liao Pan show tubes containing carotenoid extracts from S359A tomato fruits and the control.
The School of Biological Sciences, Faculty of Science, the University of Hong Kong (HKU), in collaboration with the Institut de Biologie Moléculaire des Plantes (CNRS, Strasbourg, France), has identified a new strategy to simultaneously enhance health-promoting vitamin E by ~6-fold and double both provitamin A and lycopene contents in tomatoes, to significantly boost antioxidant properties.
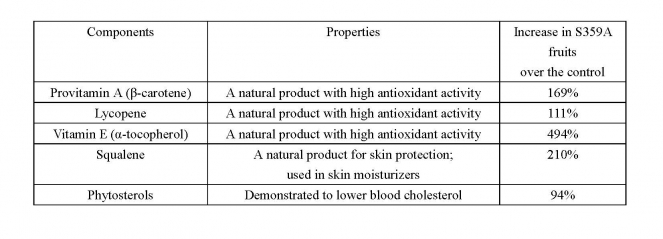
The research group manipulated the plant isoprenoid pathway through the utilization of a variant of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A synthase (HMGS). The overexpression of HMGS in tomatoes increased not only phytosterols, squalene, provitamin A and lycopene, but also vitamin E (α-tocopherol) by 494% (Table 1; Figure 1).
Table 1 Increases in provitamin A, lycopene, vitamin E (α-tocopherol), squalene and phytosterols in S359A-transformed tomato fruits in comparison to the control.
The HMGS DNA used in these experiments originated from a food crop, Brassica juncea (Indian mustard), that yields edible leaves, stems and seeds, the latter used in vegetable oil production. Earlier, this research group reported that the recombinant HMGS variant S359A (in which amino acid residue “serine” at position 359 was switched to “alanine”) exhibits 10-fold higher enzyme activity. The introduction of S359A in the model plant Arabidopsis increased phytosterol content.
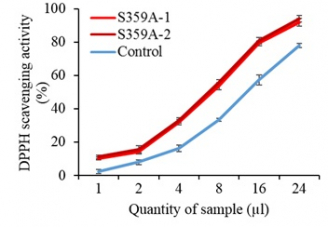
Now, the research group has introduced the S359A into tomatoes, a crop plant. Although there were no differences in the appearance and size of the transformed tomato fruits, total carotenoids including provitamin A and lycopene increased drastically by 169% and 111%, respectively, as observed by a deeper colour of carotenoid extracts in S359A tomatoes over the control (Figure 1). Furthermore, these carotenoid extracts exhibited 89.5-96.5% higher antioxidant activity than the control (Figure 2). Besides carotenoids, the transformed tomatoes displayed elevations in vitamin E (α-tocopherol, 494%), squalene (210%), and phytosterols (94%), as shown in Table 1. These observations were attributed to the increased expression of genes in the isoprenoid pathway.
Figure 1 Carotenoid extracts from S359A tomato fruits (right) show a deeper color and contain more carotenoids (provitamin A and lycopene) than the control (left). S359A-1 and S359A-2 represent two independent S359A tomato lines that give consistent results.
Figure 2 Antioxidant assays indicated that carotenoids in mature 57 days after pollination S359A tomato fruits had higher antioxidant activities than the control. S359A-1 and S359A-2 represent two independent S359A tomato lines. Antioxidant activity was defined by the ability to scavenge free radicals in DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl).
Professor Chye Mee-len who led this research said: “Increasing health-promoting components in crops is an important research area that aligns with the aspirations of Dr Wilson and Mrs Amelia Wong on the use of plant biotechnology for a sustainable future. The accumulation of the healthy components in food crops would provide added-value to fruits and vegetables in the human diet, as well as enrich feed for livestock and aquaculture.” Dr Wang Mingfu added: “Extracts with enriched phytosterols, vitamin E and carotenoids can be used in the production of anti-ageing cream and sun-care lotion. These compounds show excellent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity.”
Funded by the Wilson and Amelia Wong Endowment Fund, Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong (AoE/M-05/12), and Innovation Technology Fund of the Innovation Technology Commission (Support to Partner State Key Laboratories in Hong Kong), this research has been reported recently in Plant Biotechnology Journal http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/pbi.12828/full. The team is led by Chye Mee-len, Wilson and Amelia Wong Professor in Plant Biotechnology from the School of Biological Sciences, with two other HKU members including postdoctoral fellow Dr Liao Pan, and Associate Professor Dr Wang Mingfu, as well as Professor Thomas J Bach from the Institut de Biologie Moléculaire des Plantes, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), Strasbourg.
For details on Wilson and Amelia Wong Professorship in Plant Biotechnology, please visit: http://www.daao.hku.hk/ephku/en/Professorship-Detail/27-Wilson-And-Amelia-Wong-Professorship-In-Plant-Biotechnology.html
For the powerpoint slides on this research, please click here.
Media enquiry:
Professor Mee-len Chye, School of Biological Sciences (tel: 2299 0319; email: mlchye@hku.hk)
Dr Pan Liao, School of Biological Sciences (tel: 2299 0321; email: h1092030@connect.hku.hk)
Ms Rhea Leung, Communication and Public Affairs Office (tel: 2857 8555/ 9022 7446; email: rhea.leung@hku.hk);
Ms Cindy Chan, Faculty of Science (tel: 3917 5286/ 6703 0212; email: cindycst@hku.hk).