Media
HKU announces 2015 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast
07 Jul 2015
1 Overview
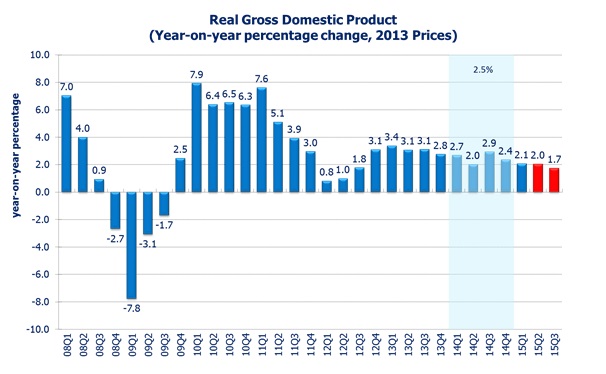
The APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) released its quarterly Hong Kong Macroeconomic Forecast today (July 7). According to its High Frequency Macroeconomic Forecast, real GDP in 15Q2 is estimated to grow by 2.0% when compared with the same period in 2014. This is a downward revision from the previous forecast release of 2.4% (April 9). This revision mainly reflects the slowdown in external demand.
In 15Q3, real GDP growth is forecast to be 1.7% when compared with the same period last year.
“Stalled external demand continues to cloud Hong Kong’s economic performance. In EU, most member countries continue to struggle for broad recovery in the first half of 2015; and Greece debt crisis remains unresolved. The Chinese economy has shown some weakness. As several shots of monetary easing were implemented, the economy seems stabilized, but a near-term rebound seems unlikely. In the US, the harsh winter and a strong dollar were the main obstacles in the first half of 2015. We believe that while the first quarter slump of US GDP is likely temporary, the growth momentum is expected to resume in the second quarter but the strong US dollar will likely hold back its recovery.
Due to Hong Kong’s peg to the US dollar, a strong US dollar will likely cause a contraction in Hong Kong’s exports of goods and services.
Taken these factors into account, Hong Kong’s economy is expected to grow at 1.7% in the third quarter of 2015, slower than the 2.0% estimated in the 15Q2,” said Dr. Wong Ka-fu, Principal Lecturer of Economics at HKU.
Among the various components, the growth in local demand is expected to cause a positive 2.9 percentage points GDP growth in 15Q3; and the external demand is expected to weigh down the GDP growth by 1.2 percentage points. The negative contribution of external demand is mainly due to the appreciation of the dollar and the slowdown of Chinese economy.
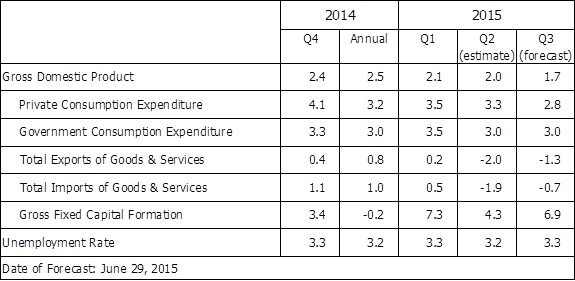
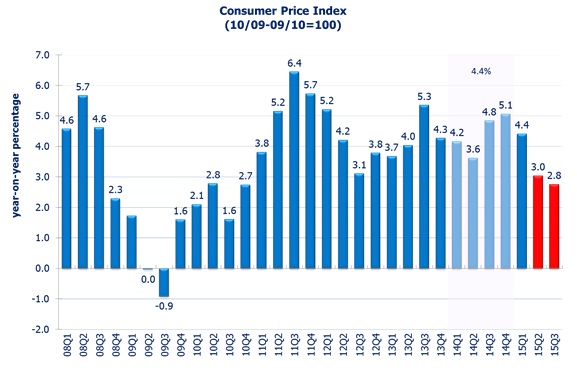
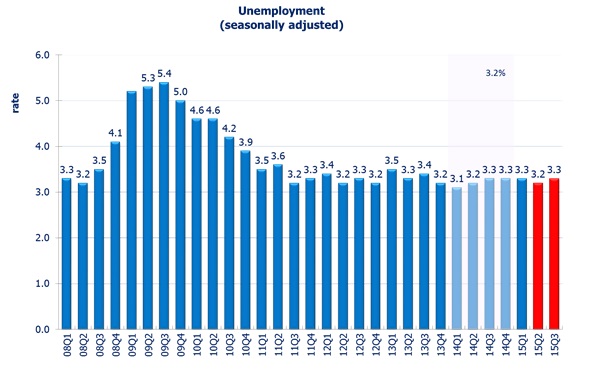
The labour market is expected to remain tight. The unemployment rate is projected to rise slightly to 3.3% in 15Q3, from 3.2% in 15Q2. With continuous government measures and lowered imported inflation due to the strong dollar, inflation is expected to ease further in the near term. The headline consumer inflation rate is forecast to be 2.8% in 15Q3.
The forecast details are in appendix Table 1 and Table 2, and the forecasts of selected monthly indicators are in Table 3 (tables attached). All growth rates reported are on a year-on-year basis.
2 Domestic Demand
2.1 Private Consumption
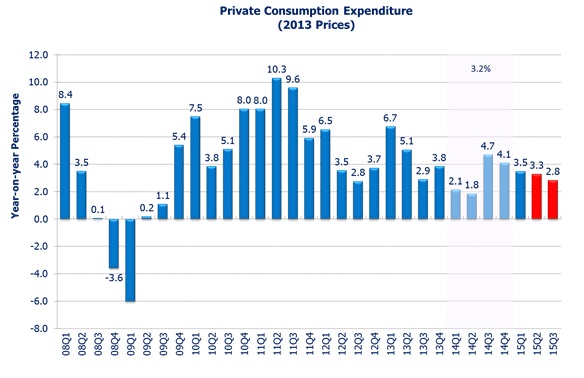
Private consumption grew by 4.1% in 14Q4, and 3.5% in 15Q1. Given the moderate output growth, growth in consumer spending is expected to be moderate in the upcoming quarters. We expect private consumption to grow at 3.3% in 15Q2 and 2.8% in 15Q3.
2.2 Retail Sales
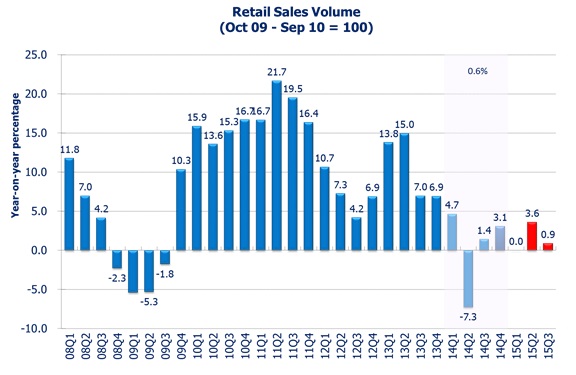
A mild increase of 2.5% in the volume of retail sales was recorded in April 2015 when compared to the same period last year. Subsequently in May 2015, a further expansion of 4.6% was recorded. The volume of retail sales is estimated to increase by 3.6% in 15Q2. Volume of retail sales in the following quarters will be constrained by the recent introduction of a more restrictive “one-week-one-visit” visa policy. Therefore, retail sales growth is forecast to rise only by 0.9% in 15Q3.
2.3 Gross Fixed Capital Formation
Gross fixed capital formation is predicted to increase by 6.9% in 15Q3, higher than the estimated 4.3% increase in 15Q2. Gross fixed capital formation in land and construction is expected to grow by 0.3% in 15Q2 and 2.7% in 15Q3. Gross fixed capital formation in machinery, equipment & computer software is expected to surge by 8.0% in 15Q2 and 11.4% in 15Q3.
3 External Demand
3.1 Goods
In the external sector, total exports of goods reverted from a 0.4% increase in 15Q1 to a 2.4% decrease in 15Q2. In particular, good exports to Mainland China dropped by 6.6% in nominal terms in May 2015 reflecting the economic slowdown of China.
Due to our peg against the US dollar, the appreciation of US dollar also greatly reduced Hong Kong price competitiveness against foreign goods. In addition, the sharp decrease of exports to mainland has contributed much to the overall decrease in our total export. Indeed, export to mainland accounts for 54% of our total export as at May 2015. Taken together, total exports of goods is expected to decrease by 2.4% in 15Q2 and 1.6% in 15Q3.
As most of the Hong Kong’s exported goods are re-exports, the imports of goods is expected to decrease by 2.6% in 15Q2 and 1.1% in 15Q3.
3.2 Services
Services exports recorded a drop of 0.6% in 15Q1. Inbound tourism growth is expected to be moderate due to the appreciation of Hong Kong dollar and the more restrictive one-week-one-visit visa policy implemented recently. Visitor arrivals grew by 3.6% in May 2015 reflecting the impact of the policy. Mainland travelers under individual visit scheme dropped by 4.8% but those not under individual visit scheme rose by 24% in May, totaled to a 5.0% growth in China visitor arrivals. This mild 5.0% growth is understood as due to the diversion of tourists to some Asian and European countries as a result of active promotion on tourism by these countries and the appreciation of Hong Kong dollar.
Slack back in goods exports also causes trade related services exports to decrease. Service exports is estimated to drop by 0.3% in 15Q2 and 0.2% in 15Q3.
Services imports recorded a growth of 4.3% in 15Q1. Outbound tourism for local citizen has increased as appreciation of the dollar makes foreign goods and services more price attractive. We expect the growth of services imports to be 4.2% in 15Q2. The growth is expected to moderate to 3.0% in 15Q3.
4 Prices
The general price level, as measured by the Composite CPI, rose by 3.1% in May 2015. The headline consumer-price based inflation rate is estimated to be 3.0% in 15Q2 and the rate would only be 2.6% in 15Q2 after stripping out the effect of rates concession and electricity subsidy implemented last year.
The appreciation of US dollar has eased the imported inflation pressure. Along with stable food and service prices, the consumer-price based inflation rate is forecast to be 2.8% in 15Q3.
5 Labour Market
The provisional seasonally adjusted unemployment rate stood at 3.2% in the three months ending in May 2015. Hong Kong’s unemployment rate has been kept under 3.5% for four consecutive years, reflecting tight labour market condition under the statutory minimum wage policy. The unemployment rate is forecast to stay at 3.2% in 15Q2.
We expect the job market to stay tight in the near future. The unemployment rate is forecast to be 3.3% in 15Q3. Comparing to 15Q2, we forecast 14,000 jobs created and 2,000 more people unemployed in 15Q3.
6 Conclusion
The effect of the US dollar appreciation on Hong Kong economy is likely to be long and variable. With the added uncertainty of the China slowdown, the delayed resolution of Greece Debt Crisis and the uncertain timing of US interest rate hike, Hong Kong economy is expected to grow moderately in 2015. Hong Kong’s real GDP is expected to grow by 2.0% in 2015 for the year as a whole, likely between 1.6% and 2.4%, slower than the 2.5% growth in 2014.
About Hong Kong Macroeconomic Forecast Project
The Hong Kong Macroeconomic Forecast is based on research conducted by the APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at HKU in the Faculty of Business and Economics. It aims to provide the community with timely information useful for tracking the short-term fluctuations of the economy. The current quarter macro forecasts have been released on a quarterly basis since 1999.
The high frequency forecasting system was originally developed in collaboration with Professor Lawrence Klein of the University of Pennsylvania in 1999-2000. Since then, the system has been maintained and further refined by the APEC Study Center which is now a research programme area of the Hong Kong Institution of Economics and Business Strategy.
The project is sponsored by the Faculty of Business and Economics and led by Dr. Ka-Fu Wong, Principal Lecturer of Economics at HKU. The Hong Kong Centre for Economic Research at HKU provides administrative support to the project. Researchers at the Hong Kong Institution of Economics and Business Strategy are solely responsible for the accuracy and interpretation of the forecasts. Our quarterly forecasts can be accessed at:
http://www.hiebs.hku.hk/apec/macroforecast.htm
For media enquiries, please contact the HKU Hong Kong Institute of Economics & Business Strategy, tel: 2548 9300, email: info@hiebs.hku.hk.